Navigation - Assisted Spine Surgery
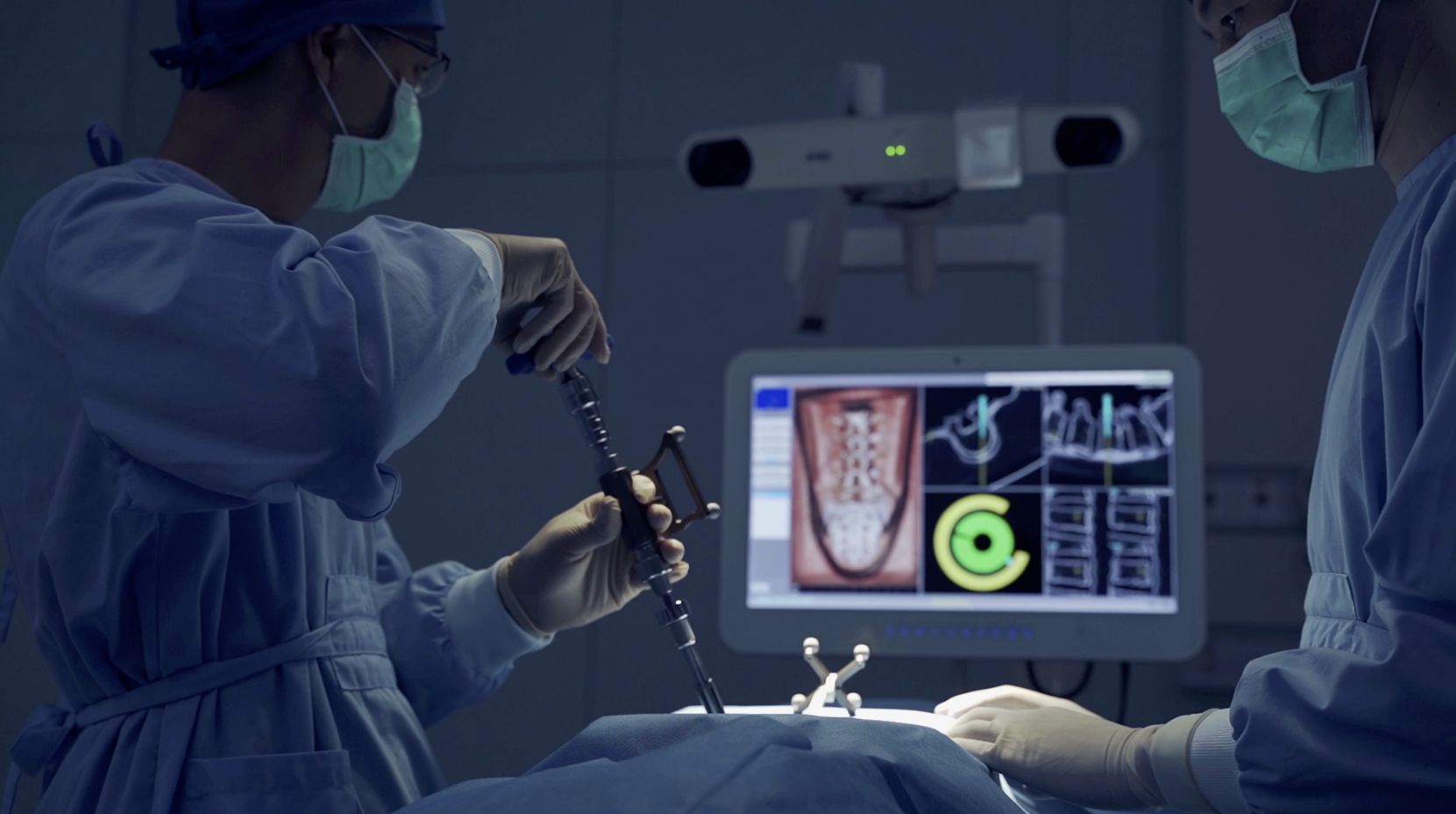
Navigation-assisted spine surgery represents a paradigm shift in surgical precision, integrating advanced computer technology to provide real-time, three-dimensional guidance during complex procedures. Often compared to a GPS system, this technology allows the surgeon to see the exact position of their instruments in relation to the patient's unique spinal anatomy on a computer screen. This virtual guidance enhances the surgeon's ability to perform delicate tasks with millimeter accuracy, significantly improving the safety and efficacy of procedures like spinal fusion and deformity correction. It is a powerful tool that helps ensure optimal placement of surgical implants while minimizing the risk to critical neural and vascular structures.
Surgical navigation begins by creating a detailed 3D 'map' of the spine using a CT or intraoperative scan. In the operating room, a special camera tracks markers on a fixed 'reference array' attached to the patient's spine and on the surgical instruments. A computer integrates this tracking data with the 3D map, allowing the surgeon to see the exact real-time position and trajectory of their tools on a monitor. This 'GPS-like' guidance enables the surgeon to execute their surgical plan with sub-millimeter precision.
TSurgical navigation offers several key advantages, primarily a dramatic increase in accuracy and safety, especially in the precise placement of pedicle screws. It is also a key enabler for Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS), providing the virtual 'eyes' needed to work through small incisions, which leads to less pain and a faster recovery. Finally, by reducing the need for repeated X-rays, it significantly reduces radiation exposure for both the patient and the surgical team.

Navigation-assisted surgery does not replace the skill of the surgeon; rather, it enhances it by providing an unprecedented level of real-time information and visual control. By transforming complex spinal procedures into more precise, safe, and reproducible operations, this technology has become a new standard of care in many centers around the world. It ultimately contributes to more reliable surgical outcomes, fewer complications, and a better overall experience for the patient.